Menü
Contact information
- Mimar Sinan Mahallesi 1359. Sokak Akademia Sağlık Merkezi No: 5 K:2 D:4 Alsancak, Konak
- info@safasatoglu.com
- Working hours: 09.00 - 18.00 Sunday: Closed
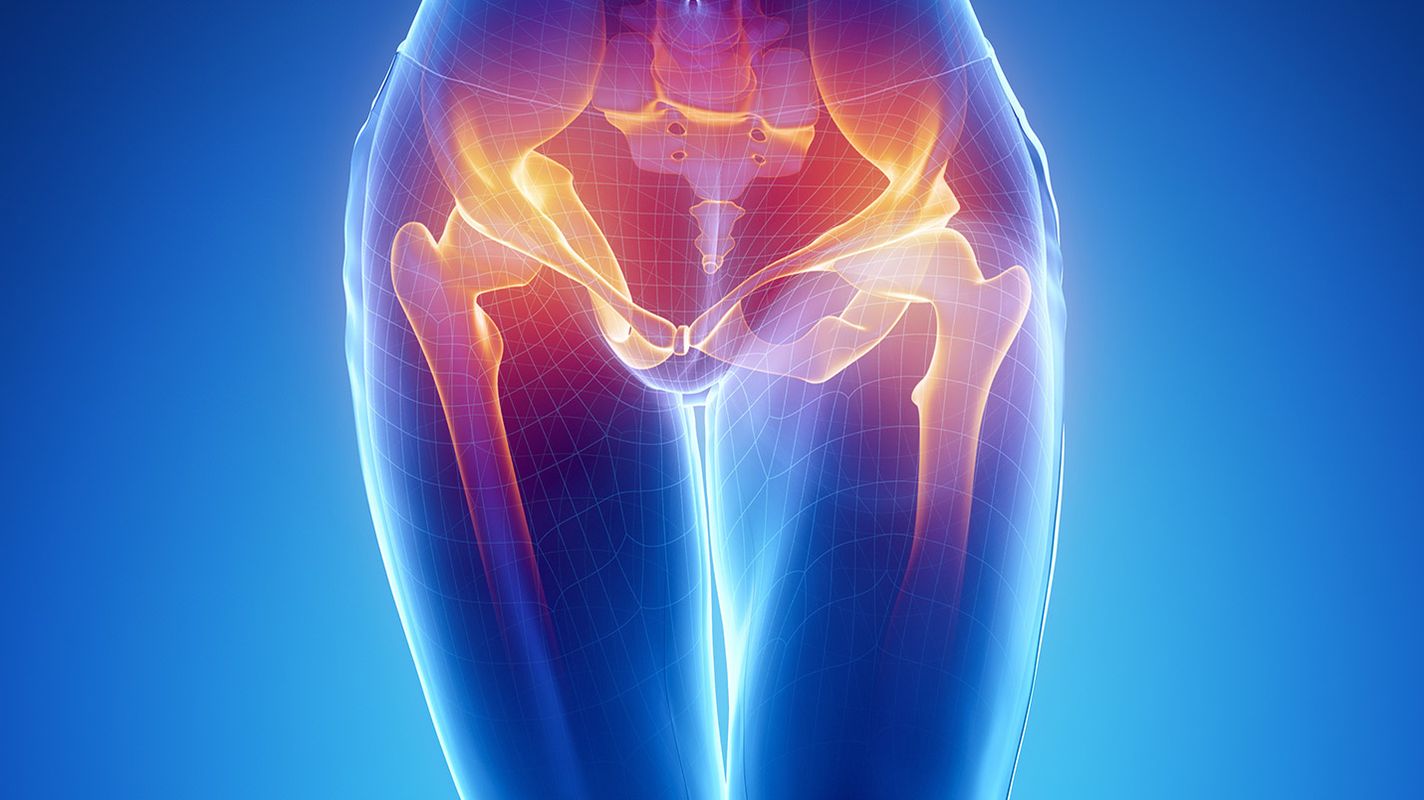
Osteoarthritis Of The Hip
- Home page
- Osteoarthritis Of The Hip
Osteoarthritis Of The Hip
As with all joints, both the ball and socket of the hip joint are covered with cartilage. The cartilage structure allows these two bones to slide over each other painlessly and with minimal friction. It is a progressive wear and tear disease of the hip bone that develops due to primary or secondary causes that disrupt the joint by involving the bone and surrounding soft tissues. This condition is called osteoarthritis in medicine, calcification in daily use and is the most common disease of the hip.
What are the Symptoms of Osteoarthritis Of The Hip?
The most important complaint is pain starting from the groin area and hitting the knee. The pain is aching and felt in the affected joint. The pain increases with movement in the initial period of the disease and decreases with rest. As the disease progresses, pain can be a problem even during simple daily activities. In more advanced stages, persistent pain may occur at night, disturbing sleep patterns. Initially, there is stiffness, pain and limping in hip movements. As the disease progresses, the hip starts to deform. The limp becomes more pronounced and that side feels as if the leg is shortened. It becomes more difficult to walk, especially up and down stairs. Hip arthritis is usually unilateral. However, deterioration of the hip on one side may affect the other hip after a while. What are the causes of osteoarthritis of the hip joint? *Inflammatory diseases (osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis etc.) * Trauma (hip circumference fractures, traumatic hip dislocation etc.) * Mechanical problems (alignment disorders in and around the hip joint, overweight, structural disorders) * Congenital hip dislocation, Perthes Clave Legg disease * Infection (after bacteria, viruses, fungal infections, etc.) * Tumors (benign and malignant tumors seen around and inside the hip)
How is Hip Osteoarthritis Diagnosed?
Physical examination and direct radiography are very useful in diagnosis. On direct radiography, narrowing of the space between the bones is observed due to damage to the joint surface. At the same time, new bone formations (osteophytes) in the form of "spurs" are seen on the edges of the joint, indicating the presence of osteoarthritis. What are the Treatment Methods in Hip Osteoarthritis? Medical Treatment: If you are in the early stages of osteoarthritis, non-surgical treatments can slow the progression of your disease, * Avoid excessive activity and loads. * Do regular physical activity. Especially swimming, water aerobics, indoor cycling maintain muscle strength and help to maintain range of motion. * Anti-rheumatic, anti-inflammatory drugs can be used. Glucosamine glycan and chondroitin sulfate, which have recently become more widely used, can also be used. These drugs have also started to gain an important place in the treatment of arthritis. * Weight loss is very important in terms of reducing the loads on the joint. * Use of a walking stick is recommended (on the right side) Surgical Treatment: In the early stages, hip arthroscopy can slow down the development of the disease. One of the surgeries before prosthesis is osteotomy. Osteotomy is the cutting and reorientation of the head or neck of the femur bone. With this method, the loads on the hip joint are rearranged and/or the intact surfaces of the joint are brought to the load-bearing areas. Although this method is becoming less popular due to the advances in total hip prosthesis, it can provide unique opportunities in some cases. Cartilage transplants performed in the early stages of osteoarthritis in small cartilage gaps (especially traumatic ones) in the femoral head of the hip joint can postpone the need for hip prosthesis to advanced ages. The radical treatment of hip osteoarthritis is total hip replacement. Replacement of the hip joint is arguably the only option for the treatment of a degenerated hip. This treatment method, which has been practiced for nearly 30 years, provides extremely good results and eliminates the physical and psychological problems caused by such a severe disease. This treatment, called "artificial joint" or "total hip replacement", is performed by replacing all the damaged and worn surfaces of the joint with metal-plastic-ceramic materials. Thanks to advances in materials science and new discoveries, the results are even more perfect today by using much higher quality and durable materials. Advanced Technology Prostheses Make Your Life Easier Hip prosthesis consists of two main parts. A socket (acetabular part) that is inserted into the pelvis and a head (femoral part) that will articulate with it and be inserted into the leg bone. These two parts of the prosthesis, made of steel, titanium or similar alloys, are inserted into the bones, which are cleaned and prepared during surgery. It is very important for a successful result that these materials are firmly held by the bone. Today, two different methods are used to achieve this. The first of these is to ensure this tight adhesion with the help of a filler called "bone cement" (polymethylmethacrylate). The other method is the cementless type of prosthesis, which has become more prominent in recent years, especially in parallel with the development of materials and engineering sciences. Here, the surface of the prosthesis is roughened with different techniques or coated with special substances that will allow the bone to adhere to the prosthesis. Thus, the prosthesis can be attached directly to the bone without the use of any filler. Between the prostheses placed in the bone prepared in this way, other materials are placed to operate the joint mechanism. Highly hard and durable special plastics (polyethylene), ceramics with reduced brittleness and increased lubricity, and sometimes even metal surfaces with the same properties are used to ensure joint function. Thanks to new methods, patients can be ambulated the day after surgery and return to their daily lives as soon as possible. Patients who are trained for regular muscle exercises and issues to be considered in the postoperative period are sent home within 4-5 days on average. What is knee arthritis? Calcification or arthritis is the deterioration of the shiny and smooth structure of the knee joint cartilage and the deterioration of the joint's functions. Patients are then ambulated and return to their daily lives as soon as possible. Patients who are trained for regular muscle exercises and issues to be considered in the postoperative period are sent home within 4-5 days on average.
What is knee arthritis?
Calcification or arthritis is the deterioration of the shiny and smooth structure of the knee joint cartilage and the deterioration of the joint's functions. In arthritis, tears in the meniscus and the formation of bone spurs usually occur together with the cartilage. Pain starts in the calcified knee. Over time, joint movements are restricted and legs start to bend as arthritis progresses. Knee Osteoarthritis Symptoms Pain and stiffness in the joints is the first symptom of the disease. As the disease progresses, joint movements are restricted and it becomes difficult to walk and climb up and down stairs. Sometimes there may be limping. The order of the joint is disrupted, there may be bending in the legs. There may be swelling inside the joint, behind the knee and in front of the joint. In advanced and unrehabilitated knees, straightening or bending the knee can be difficult and painful.
How is knee arthritis diagnosed?
Usually, the patient's statement, examination, and X-rays are sufficient. To assess the status of the ligaments and menisci, an MRI may be required. Knee Osteoarthritis Treatment Options Treatment for osteoarthritis should focus on the patient's complaints rather than radiologic findings.It can be said that the simplest treatment that relieves the patient's pain and improves the standard of living is the best treatment. Weight loss: Reducing the ideal weight of patients to their ideal weight reduces the loads on the knee, reduces the progression of the disease and increases the effectiveness and duration of the treatment methods applied. When losing weight, it is recommended to lose weight under the control of a dietician. It is recommended to lose weight slowly over a long period of time in the applied diets. Exercise and walking: Patients with arthritis can walk. While some doctors impose a ban on this, some doctors recommend walking and patients are confused. The most important criterion here is pain. You can walk distances that do not cause pain during and after walking every day. If you have pain, do not force it. The pain criterion applies to all sportive activities. For example, people with knee arthritis can play sports such as tennis and golf as long as they do not cause pain. When they experience pain, they can reduce the duration of their activities and continue to do them. If you want to do a sportive activity or if you have too much pain to walk, indoor bicycles are a very effective exercise tool. When choosing your indoor bicycle, choose a model where the pedal is in front of the seat instead of the classical bicycle model, which will allow you to use it at a later age and reduce the likelihood of back problems. Pain medication: Painkillers are the first choice of medication. Simple painkillers such as paracetamol and aspirin are initially very effective. Rheumatism medications (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) are a good option and control the patient's pain at many stages. However, their side effects on the stomach can be problematic with long-term use. Non-pharmaceutical nutritional supplements (glaucosamine and chondroitin) can be given to slow down cartilage deterioration in early osteoarthritis. Intra-articular injections are mostly used in moderate osteoarthritis when there is no acute attack and the pain is partially under control. In our clinic, both hyaluronic acid, which is the intra-knee fluid, and platelet-rich plasma (PRP), which is obtained after centrifugation of blood taken from the patient at high speed, are injected into the joint. Intra-articular steroid injections are recommended for patients with very advanced stages and medically inoperable patients. Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation: Physical therapy and rehabilitation can be very effective in the initial stages of arthritis, especially arthritis below the kneecap. In the later stages, the effect of physical therapy decreases. Surgical Treatment Options Surgical treatment options for arthritis in the knee joint can be summarized as arthroscopic cleaning of the deteriorated cartilage and washing the joint-disrupting fluids in the joint, reshaping of the bones if there is a malalignment between the thigh and tibia in the knee joint, half or full knee prosthesis surgeries and cartilage transfer according to the amount of deteriorated cartilage. The method of surgical treatment varies according to the stage of the disease. Arthroscopic Cleaning In early stage arthritis patients, arthroscopic cleaning of the inside of the knee is especially useful in patients who experience a mechanical snapping sensation. Osteotomy operations to eliminate malalignment The knee joint consists of two main areas: the inner and the outer part. Osteoarthritis starts from the inner part, which is more heavily loaded. Over time, the wear on the cartilage causes more load on the inner part of the knee and the disease progresses rapidly in this way. In patients with mid-stage arthritis, where there is not much angulation, the center of gravity can be shifted back to the middle part of the knee by reshaping the bones. Thus, the existing complaints are reduced and the progression of the disease is slowed down. Prosthetic Surgery In patients with advanced osteoarthritis, prosthetic surgery should be considered if the complaints of the patients cannot be controlled with other treatment options. Generally, these patients have to take painkillers constantly, their daily life comfort is impaired due to knee pain, and they have difficulty in walking and doing their daily work. In relatively early stage patients where only the inner part of the knee joint is affected, prostheses called half-type prostheses (unicondylar) may be preferred. Thus, the complaints of the patients are eliminated with a smaller surgery compared to a full joint prosthesis and the time of full joint prosthesis application can be postponed to later stages. Knee replacement surgeries are preferred more by patients and surgeons because they allow joint movement very early, the patient can load and walk the day after surgery and rehabilitation is easier. Both half and full knee replacements are successfully performed in our clinic.
 Turkish
Turkish English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Русский
Русский عربى
عربى